INDICATION1
ORIAHNN® (elagolix, estradiol, and norethindrone acetate capsules; elagolix capsules) is indicated for the management of heavy menstrual bleeding associated with uterine leiomyomas (fibroids) in premenopausal women. Use of ORIAHNN should be limited to 24 months due to the risk of continued bone loss, which may not be reversible.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION1
THROMBOEMBOLIC AND VASCULAR EVENTS
Estrogen and progestin combinations, including ORIAHNN, increase the risk of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders, including pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, stroke, and myocardial infarction, especially in women at increased risk for these events.
ORIAHNN is contraindicated in women with current or a history of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders and in women at increased risk for these events, including women over 35 years of age who smoke and women with uncontrolled hypertension.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- ORIAHNN is contraindicated in women at a high risk of arterial, venous thrombotic, or thromboembolic disorders; who are pregnant; with known osteoporosis; current or history of breast cancer or other hormonally sensitive malignancies; known hepatic impairment or disease; undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding; known anaphylactic reaction, angioedema, or hypersensitivity to ingredients of ORIAHNN; or with concomitant use of organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) 1B1 inhibitors that are known or expected to significantly increase elagolix plasma concentrations.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Thromboembolic Disorders and Vascular Events
- ORIAHNN is contraindicated in women with current or a history of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders and in women at increased risk for these events. Components of ORIAHNN increase the risk of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders, including pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, stroke, and myocardial infarction, especially in women at high risk for these events. In general, the risk is greatest among women over 35 years of age who smoke, and women with uncontrolled hypertension, dyslipidemia, vascular disease, or obesity.
- Discontinue ORIAHNN if an arterial or venous thrombotic, cardiovascular, or cerebrovascular event occurs. If feasible, discontinue ORIAHNN at least 4 to 6 weeks before surgery of the type associated with an increased risk of thromboembolism, or during periods of prolonged immobilization. Stop ORIAHNN if there is sudden, unexplained partial or complete loss of vision, proptosis, diplopia, papilledema, or retinal vascular lesions and evaluate for retinal vein thrombosis immediately.
Bone Loss
- ORIAHNN is contraindicated in women with known osteoporosis. ORIAHNN may cause a decrease in bone mineral density (BMD) in some patients, which is greater with increasing duration of use and may not be completely reversible after stopping treatment.
- The impact of ORIAHNN-associated decreases in BMD on long-term bone health and future fracture risk is unknown. Consider the benefits and risks of ORIAHNN in patients with a history of low-trauma fracture or other risk factors for osteoporosis or bone loss, including those taking medications that may decrease BMD (e.g., systemic or chronic inhaled corticosteroids, anticonvulsants, or proton pump inhibitors).
- Assessment of BMD by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is recommended at baseline and periodically thereafter. Consider discontinuing ORIAHNN if the risk associated with bone loss exceeds the potential benefit of treatment. Limit the duration of use to 24 months to reduce the extent of bone loss.
Hormonally Sensitive Malignancies
- ORIAHNN is contraindicated in women with current or a history of breast cancer and in women at increased risk for hormonally sensitive malignancies, such as those with mutations in BRCA genes.
- The use of estrogen alone and estrogen plus progestin has been reported to result in an increase in abnormal mammograms requiring further evaluation. Surveillance measures, such as breast examinations and regular mammography, are recommended. Discontinue ORIAHNN if a hormonally sensitive malignancy is diagnosed.
Suicidal Ideation, Suicidal Behavior, and Exacerbation of Mood Disorders
- Depression, depressed mood, and/or tearfulness were reported at a higher incidence in women taking ORIAHNN (3%) compared with placebo (1%) in the Phase 3 clinical trials. Suicidal ideation and behavior, including a completed suicide, occurred in women treated with lower doses of elagolix in clinical trials conducted for a different indication.
- Promptly evaluate patients with depressive symptoms to determine whether the risks of continued therapy outweigh the benefits. Patients with new or worsening depression, anxiety, or other mood changes should be referred to a mental health professional, as appropriate.
- Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention for suicidal ideation and behavior. Reevaluate the benefits and risks of continuing ORIAHNN if such events occur.
Hepatic Impairment and Transaminase Elevations
- ORIAHNN is contraindicated in women with known hepatic impairment or disease.
- Transaminase elevations in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) occurred with ORIAHNN in Phase 3 clinical trials. No pattern in time to onset of these liver transaminase elevations was identified. Transaminase levels returned to baseline within 4 months after peak values in these patients.
- Instruct patients to promptly seek medical attention in case of symptoms or signs that may reflect liver injury, such as jaundice.
Elevated Blood Pressure
- ORIAHNN is contraindicated in women with uncontrolled hypertension. Maximum mean increases in systolic blood pressure occurred at Month 5, and a mean maximum increase in diastolic blood pressure occurred at Month 4 in ORIAHNN-treated women, as compared to placebo-treated women.
- For women with well-controlled hypertension, continue to monitor blood pressure and stop ORIAHNN if blood pressure rises significantly. Monitor blood pressure in normotensive women treated with ORIAHNN.
Gallbladder Disease or History of Cholestatic Jaundice
- Studies among estrogen users suggest a small increased relative risk of developing gallbladder disease. For women with a history of cholestatic jaundice associated with past estrogen use or with pregnancy, assess the risk-benefit of continuing therapy. Discontinue ORIAHNN if jaundice occurs.
Change in Menstrual Bleeding Pattern and Reduced Ability to Recognize Pregnancy
- ORIAHNN may delay the ability to recognize the occurrence of a pregnancy because it may reduce the intensity, duration, and amount of menstrual bleeding. Perform pregnancy testing if pregnancy is suspected and discontinue ORIAHNN if pregnancy is confirmed.
- The effect of hormonal contraceptives on the efficacy of ORIAHNN is unknown. Advise women to use non-hormonal contraception during treatment and for 28 days after discontinuing ORIAHNN.
Effects on Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism
- ORIAHNN may decrease glucose tolerance and result in increased glucose levels. More frequent monitoring in ORIAHNN-treated women with prediabetes and diabetes may be needed.
- In women with preexisting hypertriglyceridemia, estrogen therapy may be associated with elevations of plasma triglycerides leading to pancreatitis. Use of elagolix is associated with increases in total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and serum triglycerides. Monitor lipid levels and consider discontinuing ORIAHNN if hypercholesterolemia or hypertriglyceridemia worsens.
Alopecia
- In Phase 3 clinical trials, more women experienced alopecia, hair loss, and hair thinning with ORIAHNN (3.5%) compared to placebo (1.0%). In almost one-third of affected ORIAHNN-treated women, alopecia was the reason for discontinuing treatment. No specific pattern was described. In the majority of these women, hair loss was continuing when ORIAHNN was stopped. Whether the hair loss is reversible is unknown. Consider discontinuing ORIAHNN if hair loss becomes a concern.
Effect on Other Laboratory Results
- The use of estrogen and progestin combinations may raise serum concentrations of binding proteins (e.g., thyroid-binding globulin, corticosteroid-binding globulin), which may reduce the free thyroid or corticosteroid hormone levels. Patients with hypothyroidism and hypoadrenalism may require higher doses of thyroid hormone or cortisol replacement therapy, respectively.
- The use of estrogen and progestin may also affect the levels of sex hormone-binding globulin, coagulation factors, lipids, and glucose.
RISK OF ALLERGIC REACTIONS DUE TO THE INACTIVE INGREDIENT (FD&C YELLOW NO. 5)
- ORIAHNN contains FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine), which may cause allergic-type reactions (including bronchial asthma) in certain susceptible persons. Although the overall incidence of FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) sensitivity in the general population is low, it is frequently seen in patients who also have aspirin hypersensitivity.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
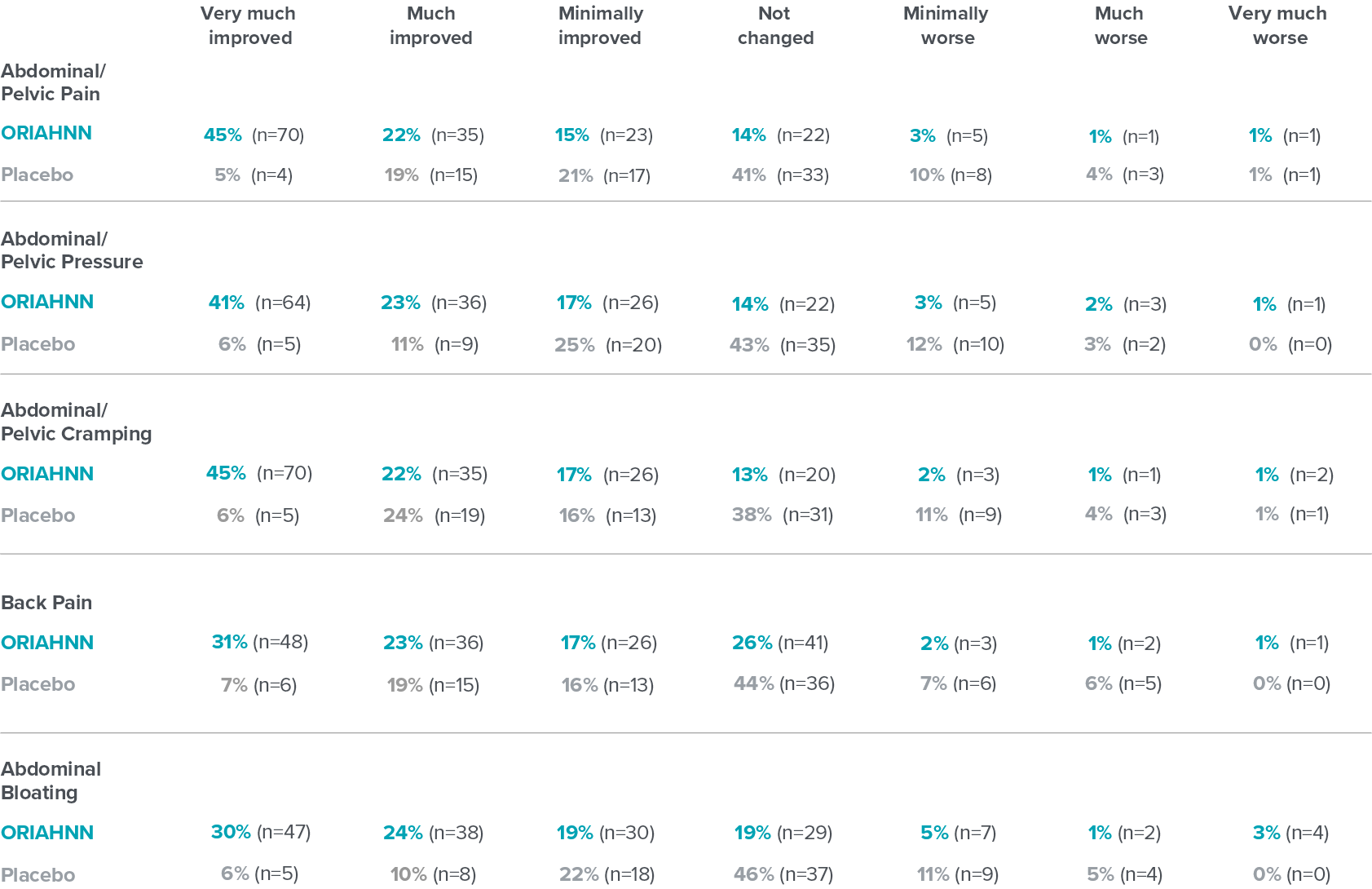
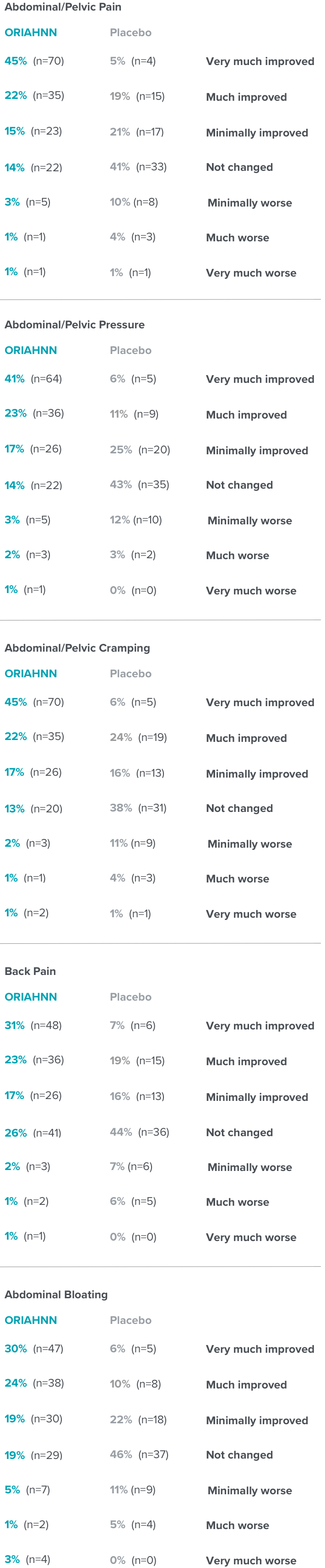
- Most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥5% of women receiving ORIAHNN in clinical trials were hot flush, headache, fatigue, and metrorrhagia.
These are not all of the possible side effects of ORIAHNN.
Safety and effectiveness of ORIAHNN in pediatric patients have not been established.
US-ORIA-210460
Please see Full Prescribing Information.